In today’s fast‑paced online environment, cybermarketing has emerged as a vital strategy for businesses aiming to reach audiences more effectively. Cybermarketing goes beyond traditional digital marketing by weaving together advanced technologies, data analytics, and creative outreach in cyberspace. In this article, we explore fundamentals of cybermarketing, its benefits, core tactics, challenges, and best practices.
1. Understanding Cybermarketing
1.1 Defining Cybermarketing
Cybermarketing refers to the strategic use of internet‑based channels and cyber infrastructure to promote products or services. Unlike conventional marketing, cybermarketing emphasizes interactions in virtual environments—social media platforms, email ecosystems, search engines, websites, and emerging immersive spaces.
1.2 Cybermarketing vs. Traditional Digital Marketing
While often used interchangeably with digital marketing, cybermarketing highlights a stronger focus on cybersecurity, data privacy, automation, and real‑time responsiveness. Cybermarketing campaigns may rely heavily on AI‑powered targeting and encryption protocols to build trust and efficiency.

2. Benefits of Cybermarketing
2.1 Enhanced Targeting and Personalization
Cybermarketing enables marketers to gather rich behavioral and demographic data to craft personalized messages tailored to individual preferences and contexts. By using analytical tools, cybermarketings campaigns can adapt in real time to optimize messaging and timing.
2.2 Cost Efficiency and Scalability Through Cybermarketing
With cybermarketings, businesses can scale outreach at relatively low marginal costs. Automated workflows handle email blasts, ad placements, and social content scheduling, reducing manual labor and enabling economies of scale.
2.3 Improved Engagement and Conversion
By interacting with prospects in the virtual spaces they frequent—such as virtual events or online communities—cybermarketing helps increase engagement. Conversion rates often improve thanks to real‑time chatbots, dynamic landing pages, and personalized user experiences.
2.4 Data‑Driven Insights
One hallmark of cybermarketing is its reliance on measurable metrics—click‑through rates, bounce rates, time on page, heatmaps, and conversion funnels. These insights allow for continuous improvement and transparent ROI tracking.
3. Key Components of Cybermarketing Strategies
3.1 Content Marketing and SEO
High‑quality, relevant content remains the backbone. Cybermarketings strategies harness SEO techniques such as keyword optimization, meta‑data structuring, and link building to ensure content ranks well and attracts organic visitors.
3.2 Email and Automation Systems
Email remains central in cybermarketing due to its directness. Automated drip campaigns, behavioral triggers, and segmentation help nurture leads efficiently. Automation reduces manual intervention while increasing personalization.
3.3 Social Media and Community Building
Cybermarketing leverages social platforms not just for advertising but for building communities. Engaging posts, live events, and social listening help brands foster trust and authority in their cyber domains.
3.4 Paid Advertising and Programmatic Ads
Programmatic advertising allows real‑time bidding and hyper‑targeted campaigns. Cybermarketing uses these capabilities to deliver ads to specific user segments across networks and devices with precision.
3.5 Cybersecurity and Privacy Compliance
A distinguishing element of cybermarketings is a strong emphasis on privacy and security. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR or CCPA, data encryption in transit and at rest, and transparent user consent mechanisms help maintain trust.
4. Implementing a Cybermarketing Campaign
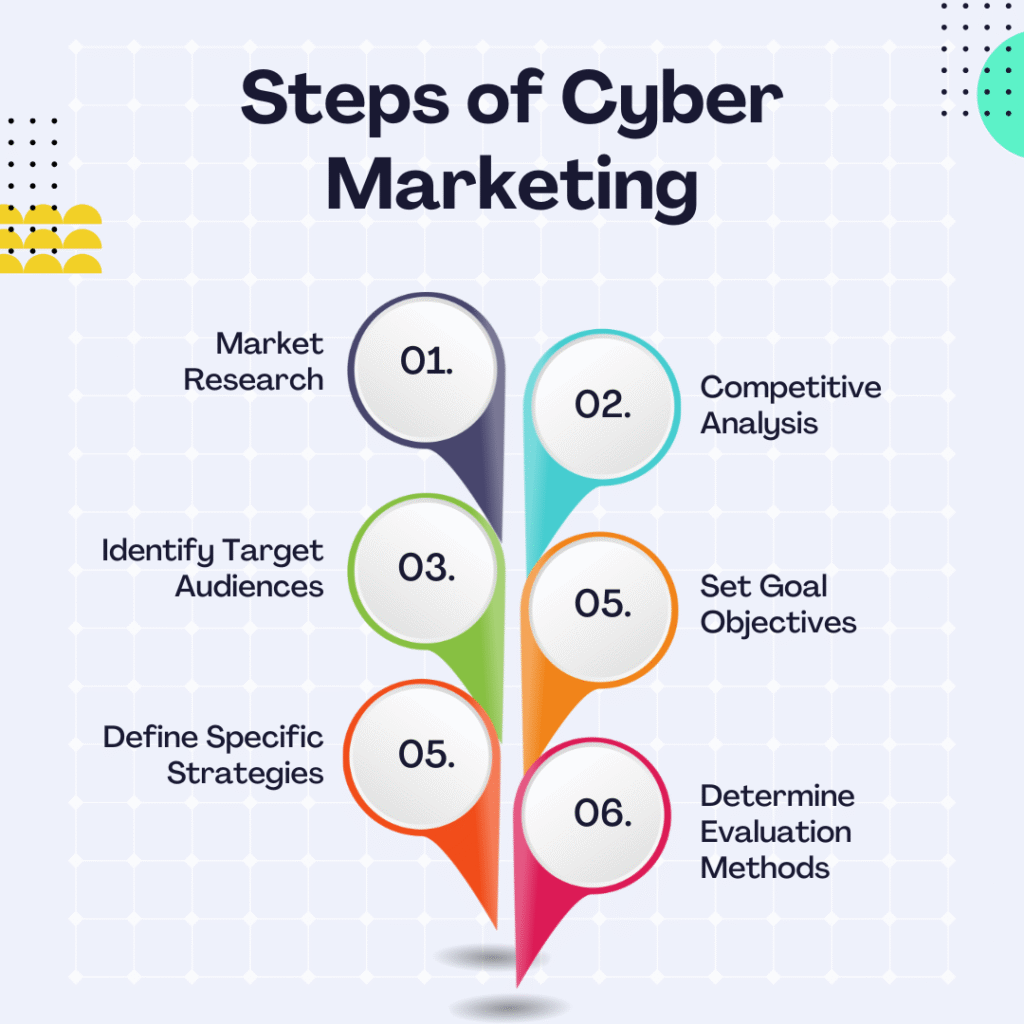
4.1 Setting Goals and KPIs
Begin with clear objectives—lead generation, brand awareness, sales, or retention. Define KPIs tied to those goals, such as conversion rate, cost per acquisition, open rate, or social engagement rate. These metrics frame your cybermarketing initiatives.
4.2 Audience Research and Persona Development
Use analytics tools to gather audience data. Identify personas based on behavior, interests, communication preferences, and cyber habits. Tailoring content to those personas is essential in cybermarketing.
4.3 Crafting Multichannel Journeys
Map out customer journeys across channels—email, social media, search ads, content hubs, chatbots. Coordinate messaging and timing so that each touchpoint reinforces the previous one; this seamless orchestration is key in cybermarketings.
4.4 Creating Engaging and Secure Content
Produce content that adds value—blogs, videos, whitepapers, interactive experiences. Embed tracking pixels responsibly, and ensure secure hosting and delivery. Cybermarketings demands both compelling storytelling and technical rigor.
4.5 Launching and Optimizing Campaigns
When live, oversee performance closely. Use A/B testing to refine emails, ad creative, subject lines, and landing pages. In cybermarketings, real‑time optimization is expected rather than occasional adjustments.
5. Measuring Cybermarketing Success
5.1 Analytical Dashboards and Reports
Dashboards showing traffic sources, campaign attribution, funnel progression, and conversion paths help marketers understand what works. Cybermarketings emphasizes transparency and data‑rich reporting.
5.2 Attribution Modeling
Applying proper attribution models—last click, multi‑touch, time decay—provides insight into which cybermarketings channels contribute most to conversion. This allows smarter budget allocation.
5.3 Privacy‑Aware Data Practices
Collecting analytics must respect user privacy. Cybermarketings campaigns use anonymized data, hashed identifiers, and explicit consent flows. This approach helps avoid regulatory fines and reputational damage.
6. Challenges in Cybermarketing
6.1 Data Privacy and Trust
Users are increasingly wary of how their data is used. Cybermarketings must balance personalization with privacy, requiring transparent consent mechanisms and data handling policies.
6.2 Ad Blockers and Platform Restrictions
Many users deploy ad blockers or privacy tools that interfere with tracking or ad delivery. Cybermarketing professionals need to craft strategies that work even in restricted environments—e.g. contextual ads, first‑party data.
6.3 Technical Complexity
Integrating multiple platforms—CRM, email, analytics, ad networks, automation—can be technically challenging. Cybermarketings may require skilled developers or IT collaboration to ensure seamless operations.
6.4 Competition and Content Saturation
As more businesses adopt cybermarketings, standing out becomes harder. Exceptional content, distinctive brand voice, and unique value propositions are needed to break through.

7. Best Practices for Effective Cybermarketing
7.1 Focus on First‑Party Data
Collect and leverage data directly from users via opted‑in responses, onsite behavior, subscriptions, and surveys. First‑party data is reliable and privacy‑compliant—a central pillar in cybermarketings.
7.2 Prioritize Security at Every Step
Ensure secure website infrastructure (HTTPS), encrypted databases, secure APIs, and safe targeting practices. Cybermarketings often involves sensitive user information—security must be baked in.
7.3 Use Automation Strategically
Automate repetitive tasks—drip emails, social posting, audience segmentation—allowing teams to focus on creative strategy. But avoid over‑automation that feels robotic or impersonal.
7.4 Test Continuously and Iterate
Run experiments—subject lines, headlines, creative options—and adapt swiftly. Cybermarketings thrives on rapid iteration. Continual testing yields better performance over time.
7.5 Blend Human Touch with Tech Capabilities
While cybermarketings uses technology heavily, human insight and creativity remain critical. Storytelling, brand voice, strategic leadership—these human dimensions differentiate top cybermarketing efforts.
7.6 Maintain Transparency and Ethics
Be upfront about data usage, cookies, tracking mechanisms, sponsorship, and opt‑out options. Ethical transparency helps build trust and long‑term relationships in cyber environments.
8. Emerging Trends in Cybermarketing
8.1 AI‑Driven Optimization
Machine learning models can predict optimal send times, content types, or targeting segments. Cybermarketings campaigns increasingly rely on AI to automate decision‑making and enhance personalization.
8.2 Immersive Experiences and Virtual Worlds in Cybermarketing
Metaverse platforms, virtual reality environments, and branded online worlds present new channels. Cybermarketings explores these spaces for interactive marketing experiences.
8.3 Voice Search and Smart Assistants
As voice interfaces like smart speakers and virtual assistants proliferate, cybermarketings strategies adapt by optimizing content and offers for voice searches and conversational interactions.
8.4 Privacy‑First Analytics
With third‑party cookies fading, cybermarketings shifts toward privacy‑first analytics—clean rooms, consent‑based tracking, and cohort analysis that respect user anonymity.
8.5 Omnichannel Cyber Integration
Cybermarketing increasingly unites digital, mobile, physical, and virtual realms. Brands orchestrate seamless experiences across chatbots, apps, websites, social platforms, and even offline touchpoints.
9. Case Example (Hypothetical)
Imagine a mid‑sized ecommerce brand launching a new product. Through cybermarketings, the brand builds targeted email sequences, deploys social media teasers, runs contextual ads, and offers immersive VR demo sessions. It collects first‑party data through sign‑ups and chat interactions, applies encryption and consent management, and measures outcomes via dashboards. Optimization in real time improves lead quality and conversion rate. The campaign combines personalization, automation, security, and multichannel outreach—hallmarks of cybermarketing.
10. Real-World Applications of Cybermarketing
10.1 E-commerce Personalization at Scale
Modern e-commerce platforms are increasingly integrating AI and machine learning into their cybermarketing strategies. For example, online stores can dynamically recommend products based on browsing behavior, previous purchases, location, and even weather. A customer in Mumbai might see monsoon-friendly products, while one in Delhi gets summerwear suggestions—all driven by intelligent algorithms behind the scenes.
10.2 SaaS Industry: Automated Lifecycle Nurturing
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies utilize cybermarketing to onboard, educate, and retain users. From automated onboarding emails triggered by signup events to in-app tutorials and webinars promoted via targeted ads, the entire user journey is orchestrated digitally. These campaigns often include real-time user tracking and behavior-based automation, ensuring timely and relevant outreach.
10.3 Education Sector: Virtual Engagement Campaigns
Universities and online learning platforms now deploy immersive cybermarketing strategies. They host virtual open houses, use chatbot-based inquiry systems, and deliver customized course recommendations based on student interests. Cybermarketing in education isn’t just about visibility—it’s about creating meaningful virtual engagement across time zones.
11. Cybermarketing Ethics and Responsible Innovation
11.1 Moving Beyond Clicks: Respect Over Manipulation
While the goal of cybermarketing is often conversion, ethical practices should always lead. This includes avoiding dark UX patterns like false urgency, misleading ad placements, or pre-checked consent boxes. Building user trust through honesty pays off with long-term brand loyalty and higher lifetime customer value.
11.2 Algorithm Bias and Fair Targeting
AI-based tools used in cybermarketing can unintentionally carry biases—excluding certain groups or unfairly favoring others. Brands must audit their targeting algorithms regularly to ensure fairness and inclusivity in ad delivery, email segmentation, and chatbot responses.
11.3 Sustainability in Digital Campaigning
Cybermarketing campaigns also contribute to carbon footprints—think of server energy consumption, email bandwidth, and constant ad refreshes. Responsible marketers now optimize campaign frequency, compress data-heavy files, and choose greener hosting providers. Sustainability is the next frontier in ethical cybermarketing.
12. Cybermarketing in the Indian Context (Optional Local Angle)
India’s growing digital population—projected to cross 1.2 billion users—makes it one of the most dynamic cybermarketing landscapes. Mobile-first campaigns, regional language content, and WhatsApp-based marketing are widely effective here. Additionally, government regulations such as the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) necessitate robust compliance in all digital activities.
- Local Platforms: Brands targeting Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities often integrate regional influencers and vernacular platforms (e.g., ShareChat) into their cybermarketing mix.
- Festive Campaigns: Indian cybermarketing strategies frequently revolve around seasonal peaks—Diwali, Holi, Independence Day—when user engagement soars.
13. Cybermarketing Skillsets for 2025 and Beyond
To run a successful cybermarketing program, professionals must build a hybrid skill set:
- Tech Knowledge: Understanding of APIs, CRM systems, AI tools, and data privacy compliance.
- Creative Thinking: Storytelling, brand positioning, and visual content development.
- Data Analysis: Interpreting dashboards, setting KPIs, and turning metrics into decisions.
- User Experience (UX): Designing seamless, secure, and intuitive interactions across platforms.
- Agile Execution: The ability to pivot based on trends, feedback, or campaign results in real time.
Brands that invest in upskilling their teams across these areas will lead the future of cybermarketing.
14. Future-Proofing Your Cybermarketing Strategy
To remain competitive, businesses must constantly audit and evolve their cybermarketing strategy. Some final recommendations include:
- Conduct quarterly privacy audits to ensure compliance and trust.
- Maintain a first-party data strategy as cookies phase out.
- Create a content library that addresses different stages of the customer journey.
- Set up scenario-based A/B testing to prepare for different market responses.
- Build a tech stack roadmap—knowing which tools to integrate and when.
Key Features of Cyber Marketing
1. Technology-Driven
Cyber marketing uses artificial intelligence, automation, and machine learning to analyze user behavior, predict trends, and deliver personalized experiences at scale.
2. Data-Centric
It heavily relies on customer data—search history, online purchases, or social media behavior—to build detailed profiles and deliver relevant campaigns.
3. Cybersecurity Awareness
Since it operates entirely in cyberspace, cyber marketing emphasizes data privacy and secure transactions, ensuring users trust the platforms they engage with.
4. Global Connectivity
Like digital marketing, it enables businesses to reach worldwide audiences, but with more precision using real-time data tracking and geo-targeted campaigns.
5. Interactive & Immersive
Cyber marketing goes beyond static ads. It includes virtual try-ons, metaverse marketing, chatbots, gamified ads, and AR/VR experiences to boost customer engagement.
Benefits of Cyber Marketing
- Enhanced Personalization – Customers receive messages that match their interests.
- High Engagement – Through interactive formats and immersive tools.
- Trust & Security – Builds confidence with privacy-focused strategies.
- Scalability – Works for startups and global brands alike.
- Real-Time Adaptability – Campaigns can be modified instantly based on performance.
Example of Cyber Marketing in Action
- E-commerce: AI-powered recommendations on Amazon.
- Finance: Secure blockchain-based loyalty programs.
- Retail: AR apps that let customers “try” clothes before buying.
- Social Media: Personalized ad placements based on browsing habits.
15. Final Thoughts
Cybermarketing represents the cutting edge of online promotion, merging technological sophistication with marketing creativity. By focusing on privacy, automation, enriched data usage, and immersive experiences, cybermarketings positions brands to connect more meaningfully with audiences. That said, it requires technical coordination, continuous testing, and ethical stewardship.
To succeed in cybermarketings, organizations must adopt a mindset of experimentation and privacy consciousness. They should harness the power of first‑party data, automation, and AI tools while maintaining a human, values‑driven voice. In doing so, cybermarketing becomes not just a buzzword, but a strategic asset for long‑term growth and digital relevance.